Publications
2026
-
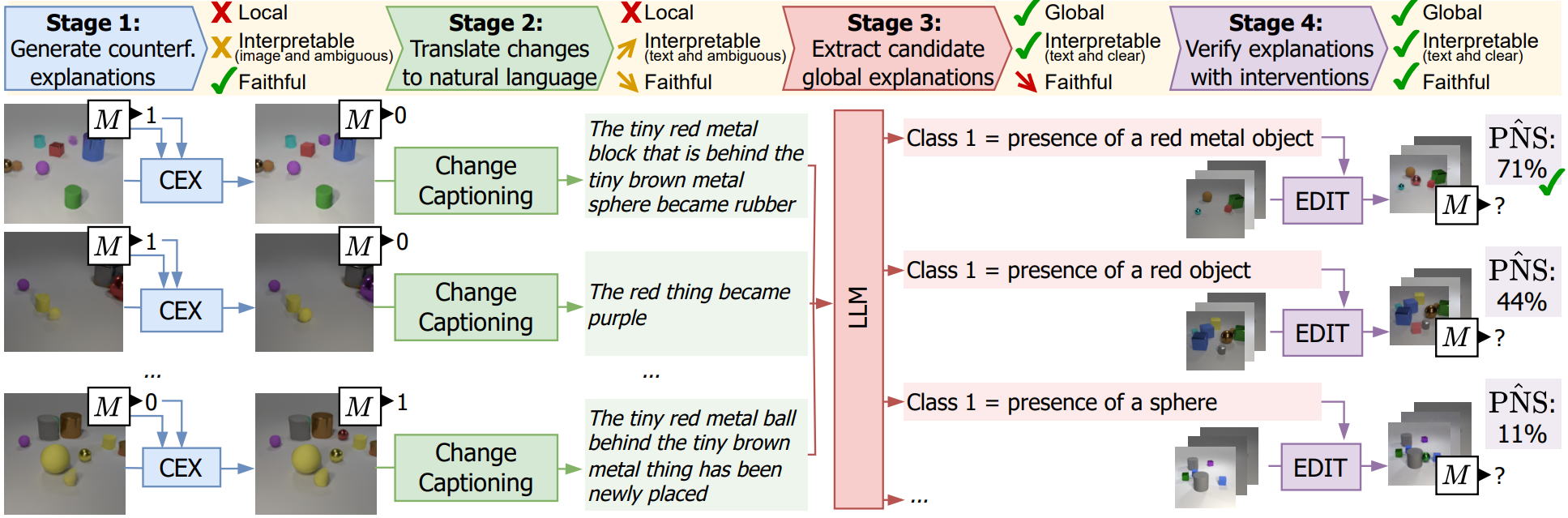
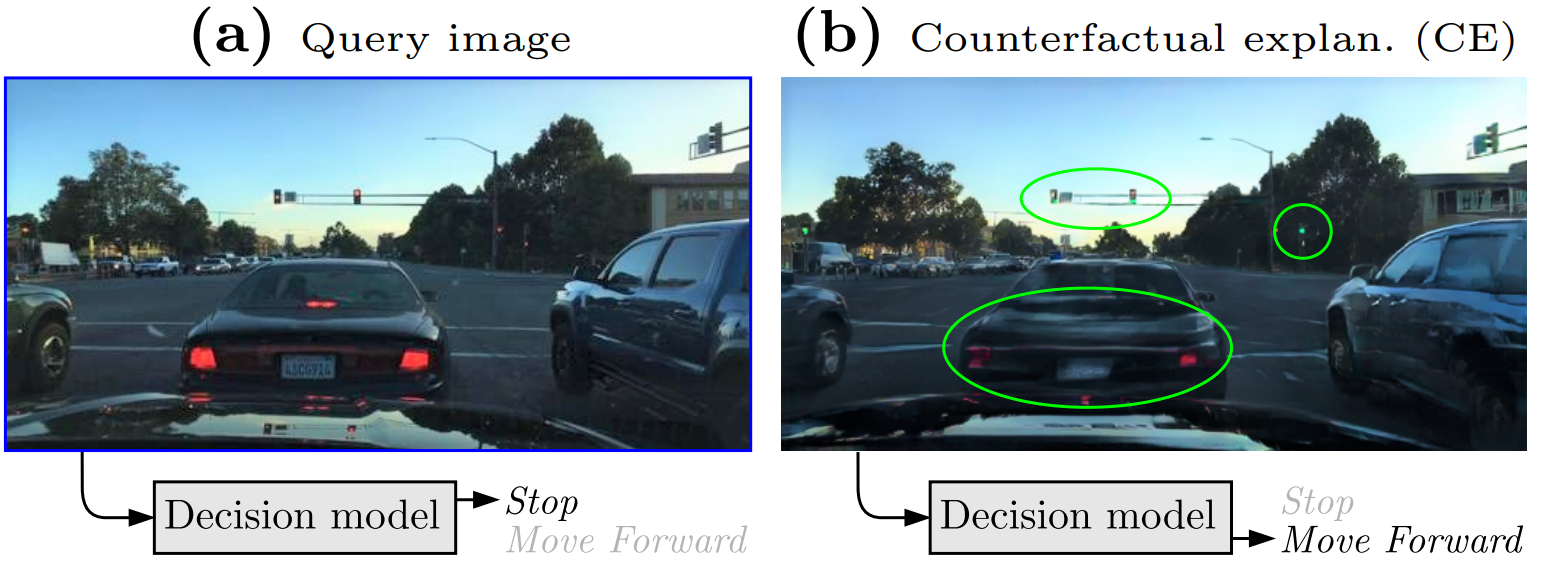
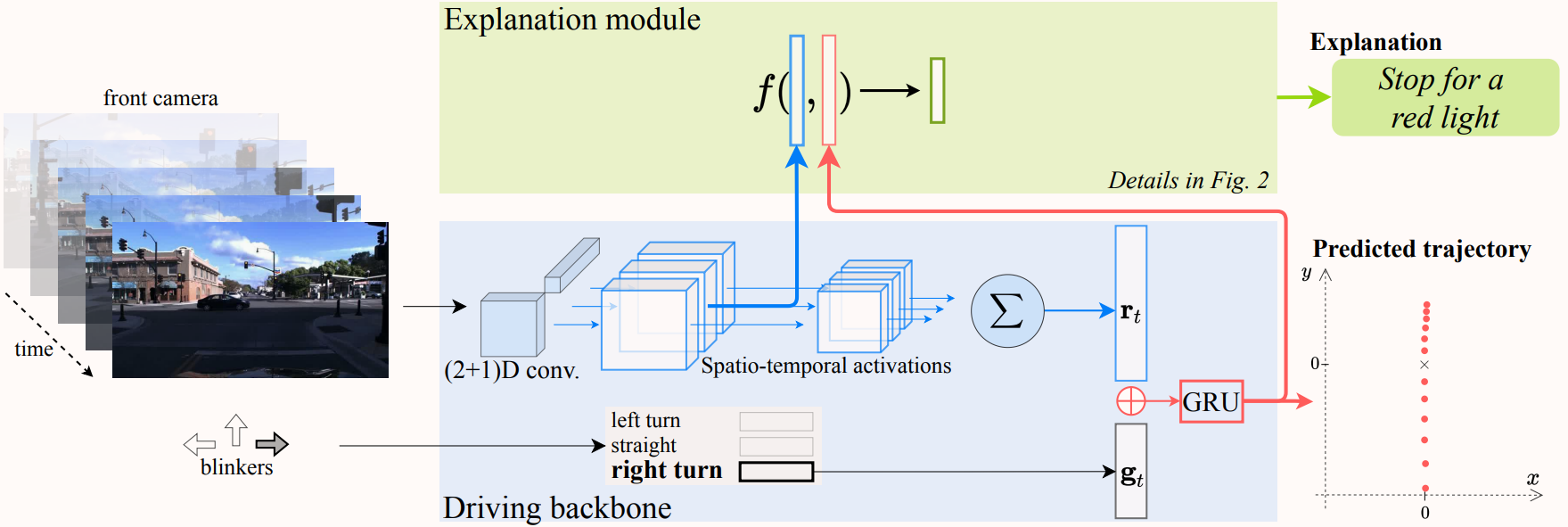
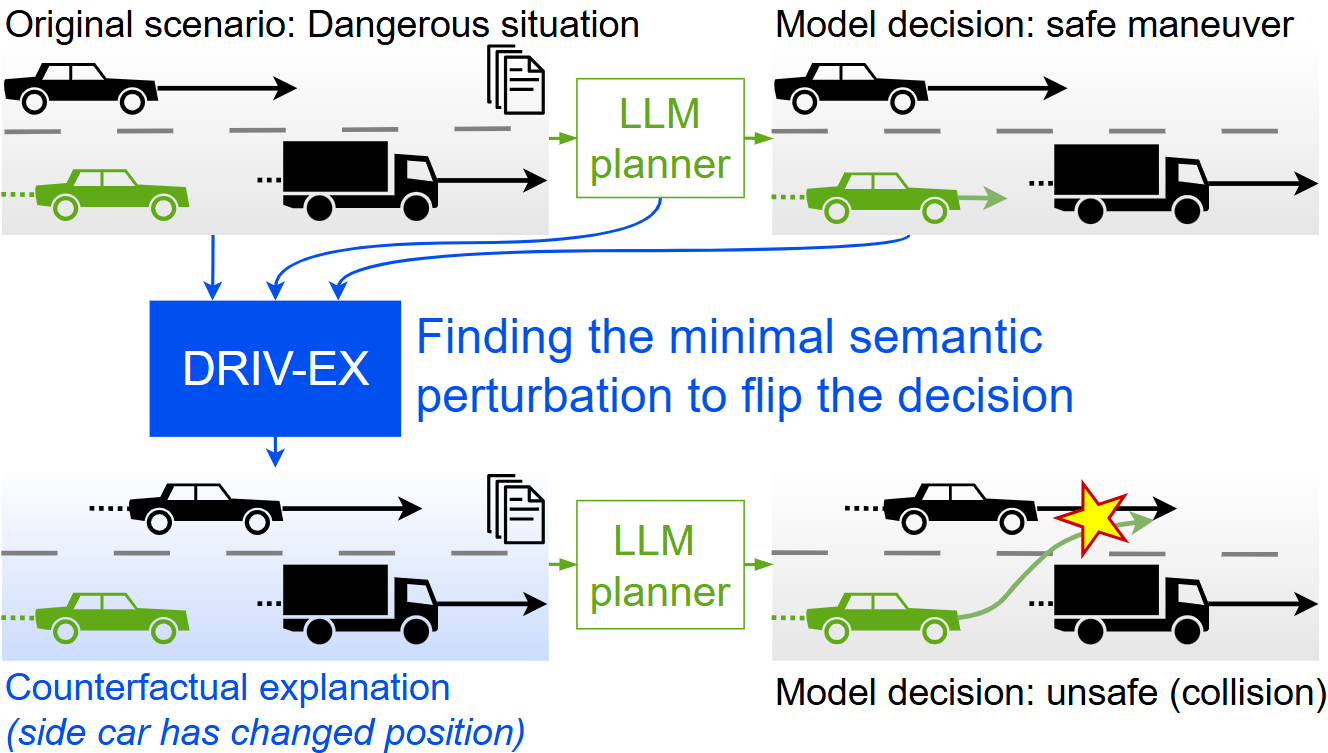 DRIV-EX: Counterfactual Explanations for Driving LLMspreprint, 2026Biasing autoregressive decoding with gradient-optimized embeddings enables the generation of counterfactual explanations to inspect the robustness and reliance on spurious biases of Driving LLMs.
DRIV-EX: Counterfactual Explanations for Driving LLMspreprint, 2026Biasing autoregressive decoding with gradient-optimized embeddings enables the generation of counterfactual explanations to inspect the robustness and reliance on spurious biases of Driving LLMs. -
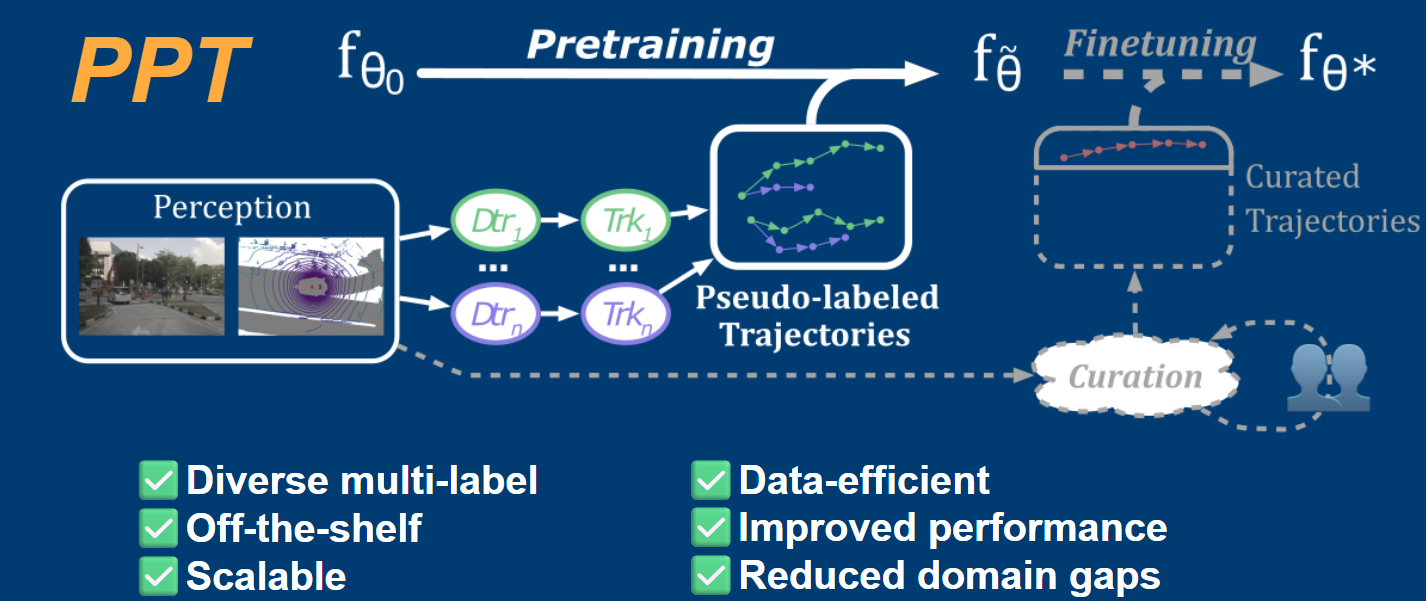
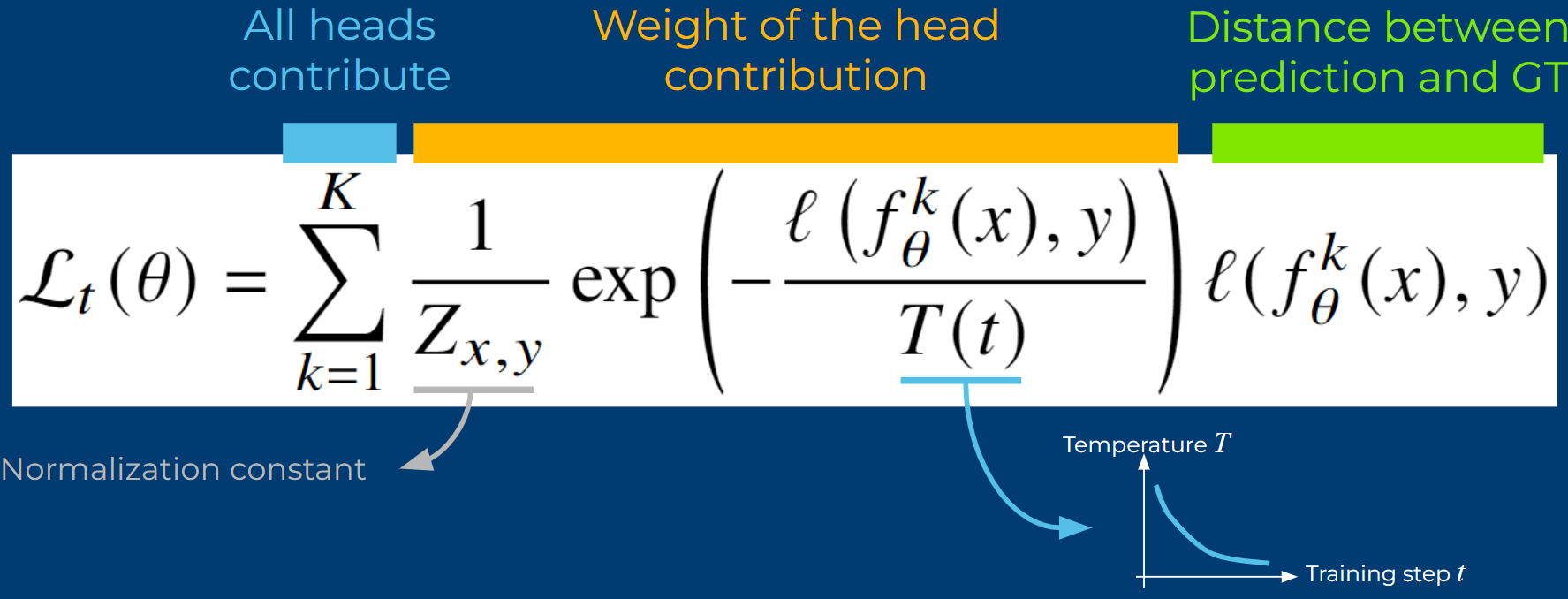
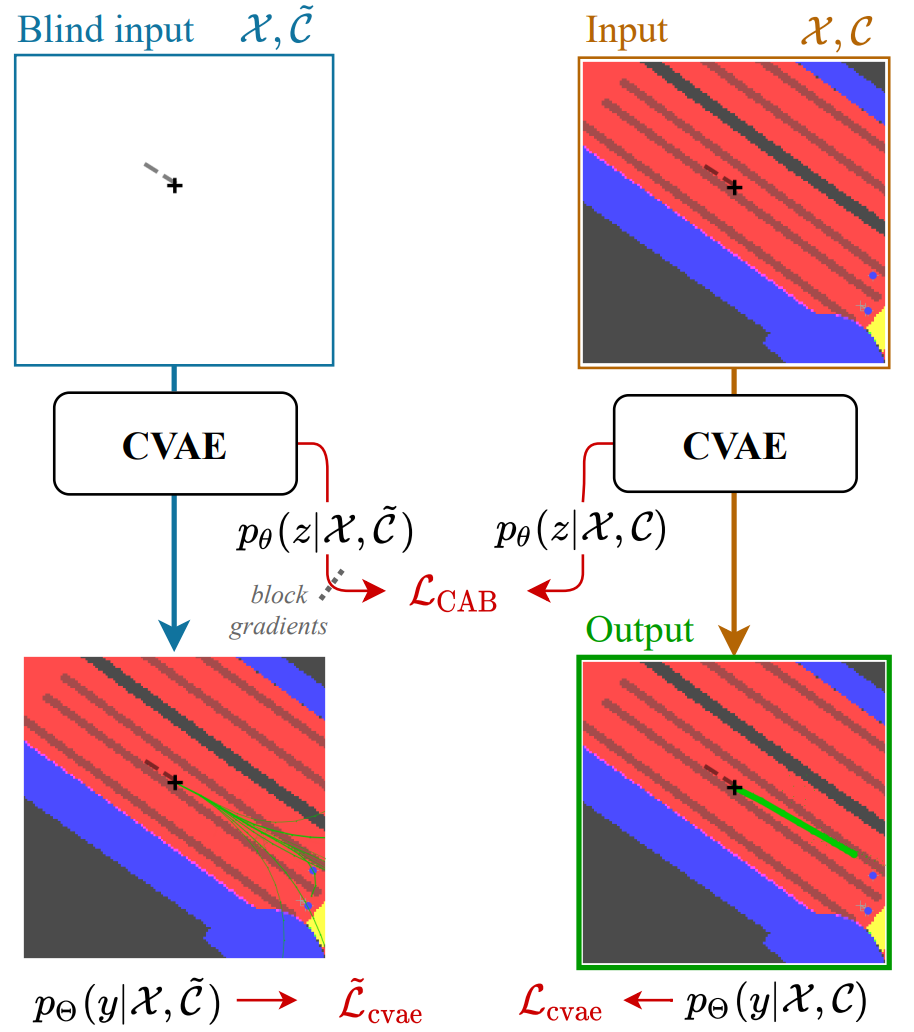
 MAD: Motion Appearance Decoupling for efficient Driving World Modelspreprint, 2026Decoupling motion learning from appearance synthesis enables efficient adaptation of general video diffusion models into controllable, state-of-the-art driving world models with minimal supervision.
MAD: Motion Appearance Decoupling for efficient Driving World Modelspreprint, 2026Decoupling motion learning from appearance synthesis enables efficient adaptation of general video diffusion models into controllable, state-of-the-art driving world models with minimal supervision.
2025
-
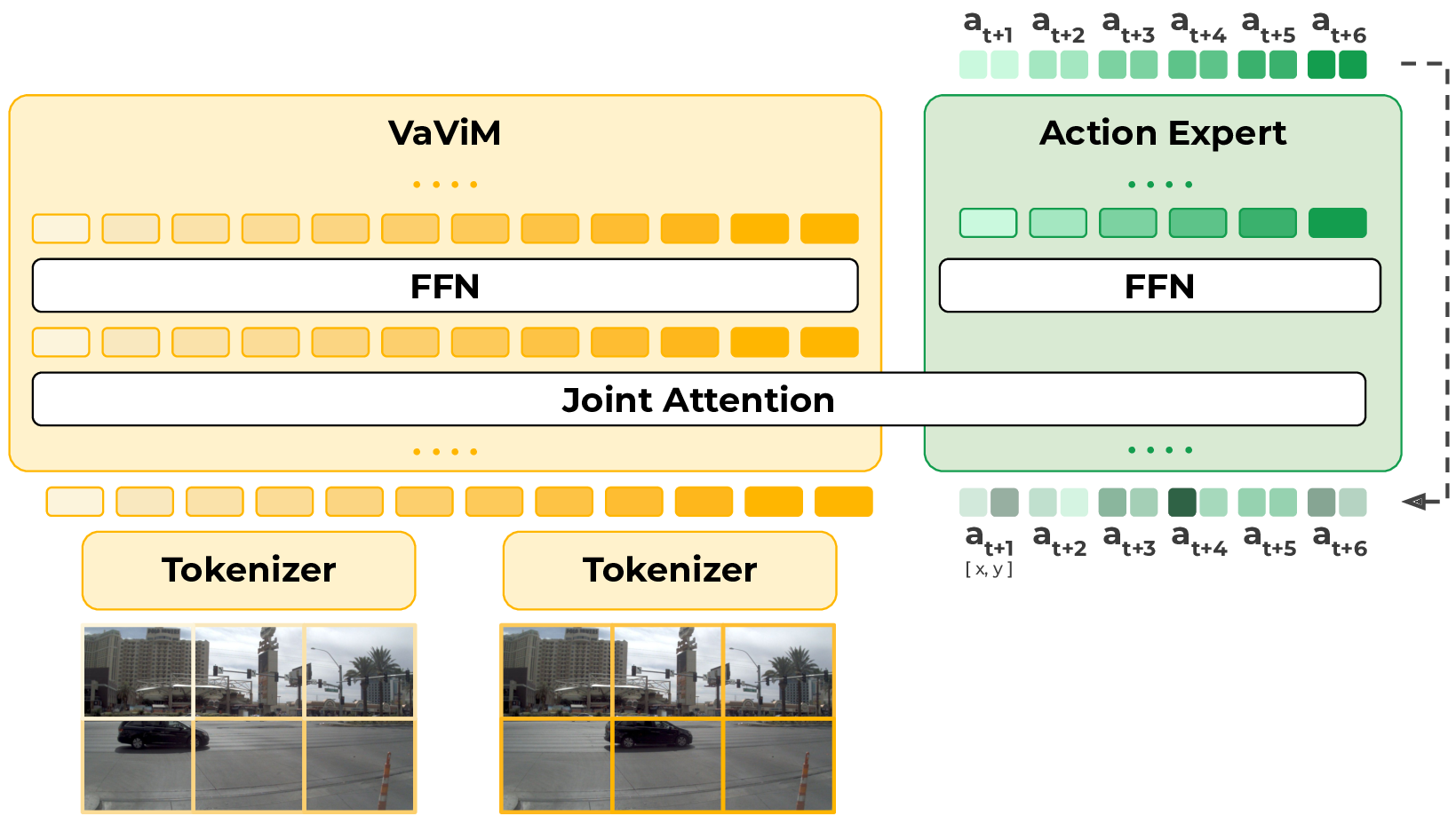 VaViM and VaVAM: Autonomous Driving through Video Generative ModelingIn CoRL Workshop on Learning to Simulate Robot Worlds, 2025Learning to drive from YouTube. VaViM, a 1.2B parameter video generative model trained on 1,800+ hours of raw YouTube driving videos, enables VaVAM, a video-action model that achieves state-of-the-art closed-loop results on driving benchmark.
VaViM and VaVAM: Autonomous Driving through Video Generative ModelingIn CoRL Workshop on Learning to Simulate Robot Worlds, 2025Learning to drive from YouTube. VaViM, a 1.2B parameter video generative model trained on 1,800+ hours of raw YouTube driving videos, enables VaVAM, a video-action model that achieves state-of-the-art closed-loop results on driving benchmark.
2024
-
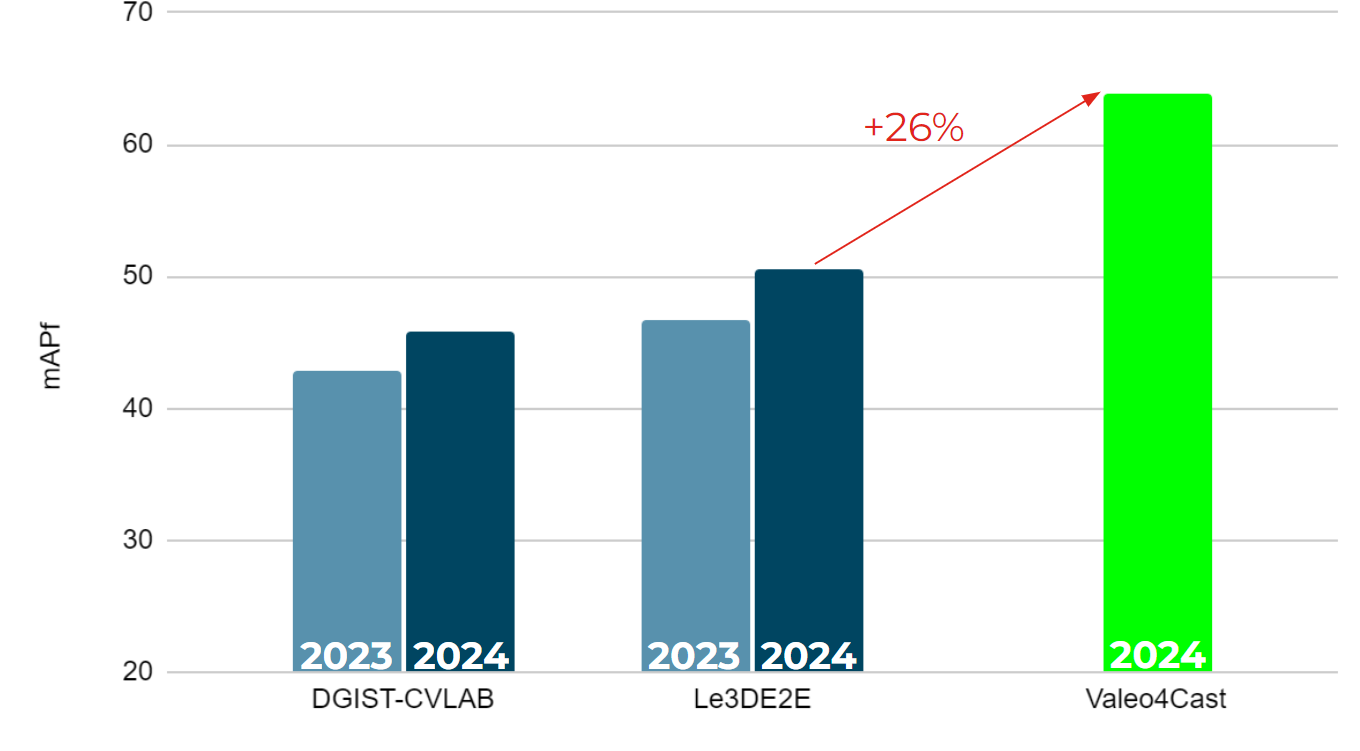 Valeo4Cast: A Modular Approach to End-to-End ForecastingIn ECCV Workshop ROAD++, 2024Using separate training and fine-tuning of detection, tracking, and forecasting modules, achieves first place in the Argoverse 2 Challenge, outperforming last year’s winner by +17.1 points.
Valeo4Cast: A Modular Approach to End-to-End ForecastingIn ECCV Workshop ROAD++, 2024Using separate training and fine-tuning of detection, tracking, and forecasting modules, achieves first place in the Argoverse 2 Challenge, outperforming last year’s winner by +17.1 points. -
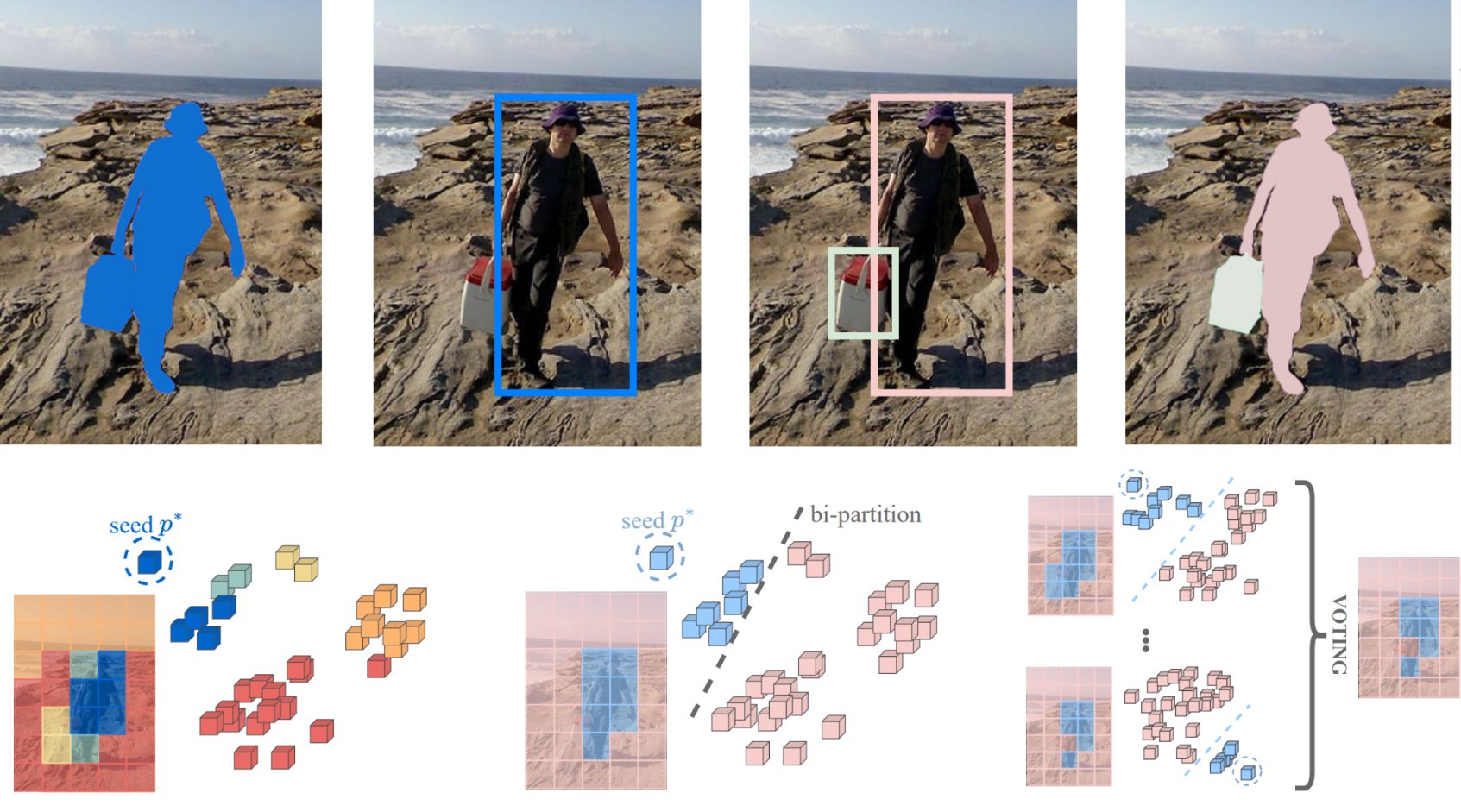
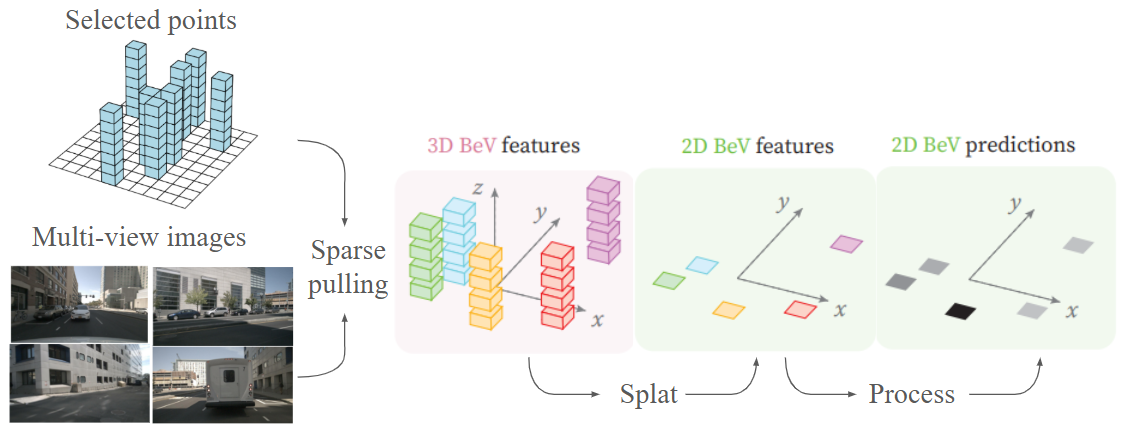 PointBeV: A Sparse Approach to BeV PredictionsIn CVPR, 2024A sparse approach to bird’s-eye view perception enhances performance and computational efficiency by avoiding the uniform allocation of resources across all cells, making it flexible to the task, situation and compute budget at inference time.
PointBeV: A Sparse Approach to BeV PredictionsIn CVPR, 2024A sparse approach to bird’s-eye view perception enhances performance and computational efficiency by avoiding the uniform allocation of resources across all cells, making it flexible to the task, situation and compute budget at inference time. -
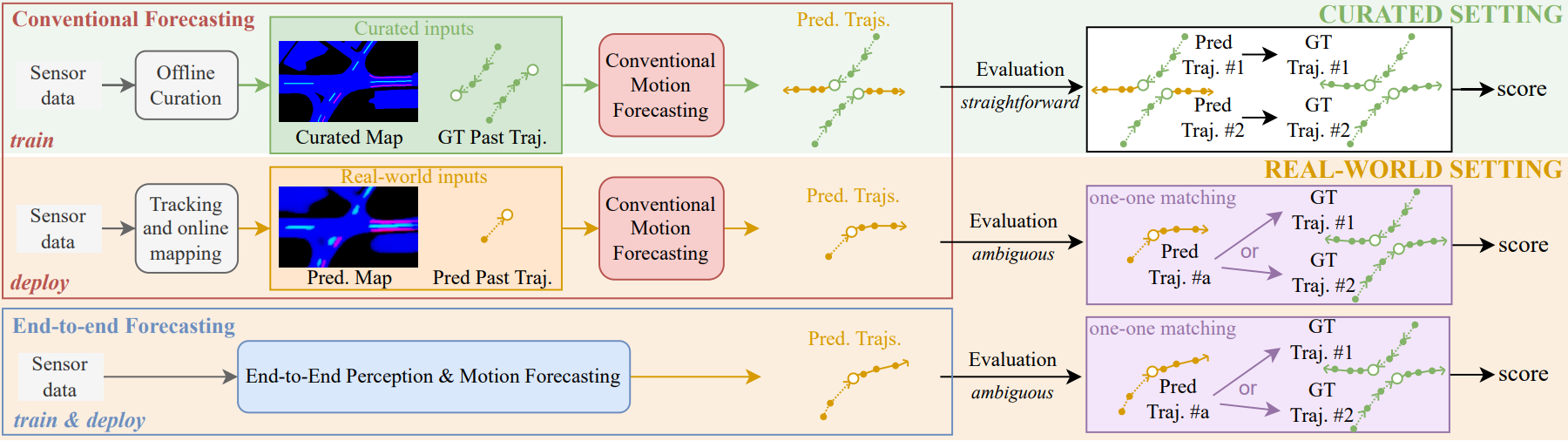 Towards Motion Forecasting with Real-World Perception Inputs: Are End-to-End Approaches Competitive?In ICRA, 2024This work presents a unified evaluation pipeline for motion forecasting with real-world perception inputs, revealing a performance gap between curated and perception-based data.
Towards Motion Forecasting with Real-World Perception Inputs: Are End-to-End Approaches Competitive?In ICRA, 2024This work presents a unified evaluation pipeline for motion forecasting with real-world perception inputs, revealing a performance gap between curated and perception-based data.
2023
2022
2020
2019
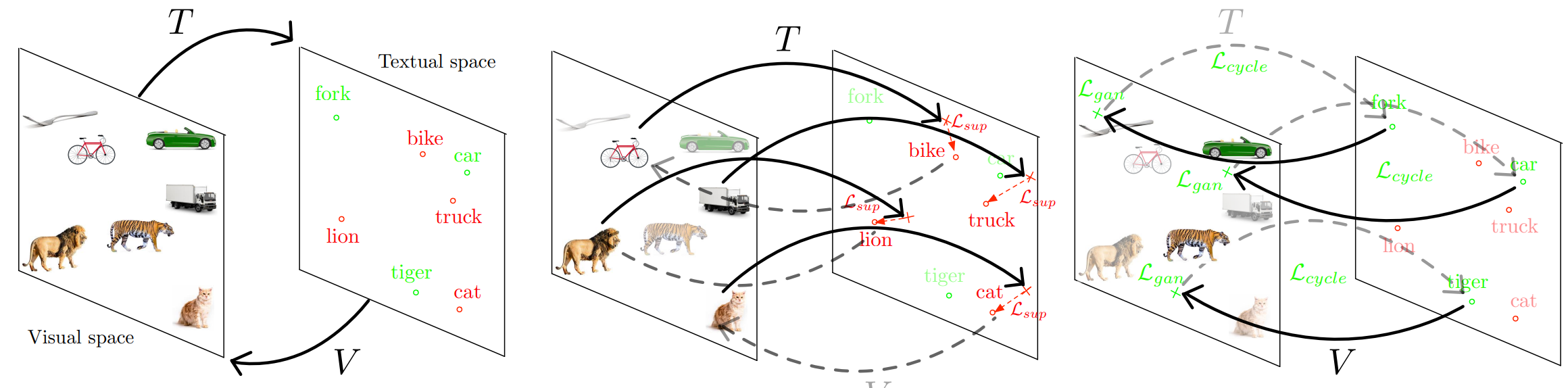
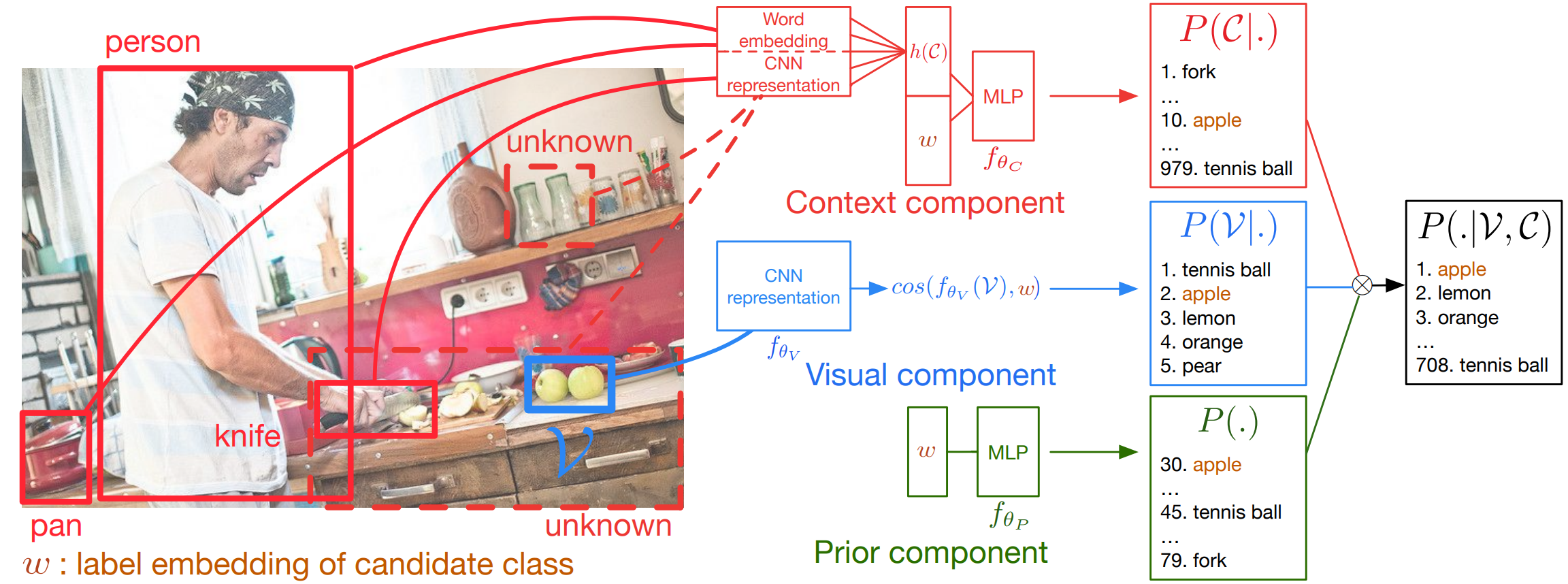
- Context-Aware Zero-Shot Learning for Object RecognitionIn ICML, 2019Using visual context boosts zero-shot object recognition.